How to Install and Use the Linux bat Command
Traducciones al EspañolEstamos traduciendo nuestros guías y tutoriales al Español. Es posible que usted esté viendo una traducción generada automáticamente. Estamos trabajando con traductores profesionales para verificar las traducciones de nuestro sitio web. Este proyecto es un trabajo en curso.
The bat command is a clone of the ubiquitous cat command. It modernizes cat with a more readable design and features like syntax highlighting and a Git integration. This guide details how bat compares with its predecessor and shows you how to install and start using it on your Linux system.
Before You Begin
If you have not already done so, create a Linode account and Compute Instance. See our Getting Started with Linode and Creating a Compute Instance guides.
Follow our Setting Up and Securing a Compute Instance guide to update your system. You may also wish to set the timezone, configure your hostname, create a limited user account, and harden SSH access.
NoteThe steps in this guide are written for a non-root user. Commands that require elevated privileges are prefixed withsudo. If you’re not familiar with thesudocommand, see the Linux Users and Groups guide.
bat vs. cat
You may be familiar with the Linux cat command. It is included in most distributions by default and gets referenced frequently as a quick way of viewing the contents of a file contents while on the command line.
Like cat, bat also gives you a simple command-line method for displaying file contents. But bat comes with a more modern display and several added features that set it apart.
For one, bat adds syntax highlighting. This, combined with other display enhancements — easier-to-follow formatting, pagination, graphical non-printing characters — makes bat exceptional for reading files that contain code.
bat also comes ready to integrate with several other command-line tools, chief among them is Git. By default, bat provides annotations to indicate modified lines for files tracked by Git. You can even use bat to view past versions of files under version control.
How to Install bat
For many Linux distributions, you can get bat from the package manager. This is the case for Debian, Ubuntu, and Fedora distributions.
For Debian and Ubuntu, install
batusing the following command:sudo apt install batOn Debian and Ubuntu,
batuses thebatcatcommand by default because of a conflict with an existing package,bacula-console-qt. You can, however, use the following commands to link thebatcommand:mkdir -p ~/.local/bin ln -s /usr/bin/batcat ~/.local/bin/batNote
If you have installed thebacula-console-qtpackage, be sure to remove it before executing the commands listed above. Otherwise, if you choose to keepbacula-console-qtinstalled, you must stick with using thebatcatcommand instead ofbat.For Fedora:
sudo dnf install bat
For AlmaLinux and CentOS, a few more steps are required. For those distributions, follow the steps below to download the appropriate bat release and install it.
If you do not already have it, install
tar, which you use to extract thebatpackage in a later step.sudo yum install tarCheck the CPU architecture of your Linux system using the following command:
uname -aHere is an example of what your output might look like.
Linux hostname 4.18.0-305.7.1.el8_4.x86_64 #1 SMP Thu Jul 1 02:00:00 EDT 2021 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/LinuxIn this example — and in the commands that follow — the CPU architecture is x86_64.
Identify the latest version of
batfrom the release page. Find the corresponding.tar.gzpackage with your system’s CPU architecture, followed byunknown-linux-muslin the name. Copy the URL for that release package. The URL is needed in the next step.Copy the package’s URL, and use the following command to download the package as
bat.zip.curl -o bat.zip -L https://github.com/sharkdp/bat/releases/download/v0.18.2/bat-v0.18.2-x86_64-unknown-linux-musl.tar.gzExtract the package.
tar -xvzf bat.zipMove the
batfiles to/usr/local.sudo mv bat-v0.18.2-x86_64-unknown-linux-musl /usr/local/batAdd an alias for
batto your.bashrcfile. Likely, the file is located in your user’s home directory, as in:~/.bashrc. You can create the alias by adding the following line to the end of the file.- File: ~/.bashrc
1 2 3 4[...] alias bat="/usr/local/bat/bat"
Once you have installed bat, by whatever method, you can verify the installation using the version command.
bat --version
bat 0.18.2How to Use bat
Getting started with bat is similar to the basic usage of the cat command. You issue the bat command, followed by the path to a file you want to view.
To really show off the capabilities of bat, this guide uses some example code provided in the
Flask-RESTful GitHub project. You can get the code by installing Git (if you do not already have it) and cloning the repository. Replace apt with dnf if you are on Fedora, and yum if you are on AlmaLinux or CentOS.
sudo apt install git
git clone https://github.com/flask-restful/flask-restful.git
Now, you can open up one of the Python files in this repository using bat.
bat flask-restful/examples/todo.py
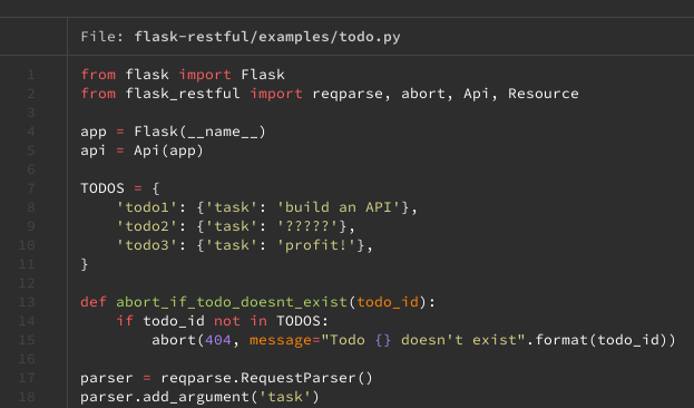
By default, bat uses less to paginate its results. However, you can also have bat print to the command line, just like in cat with the --paging=never flag.
bat --paging=never flask-restful/examples/todo.py
Like cat, bat gives the option to show non-printing characters, making it easier to track spaces, tabs, line breaks, etc. But bat has the added advantage of using special characters and highlighting to represent non-printing characters more clearly.
bat --show-all flask-restful/examples/todo.py
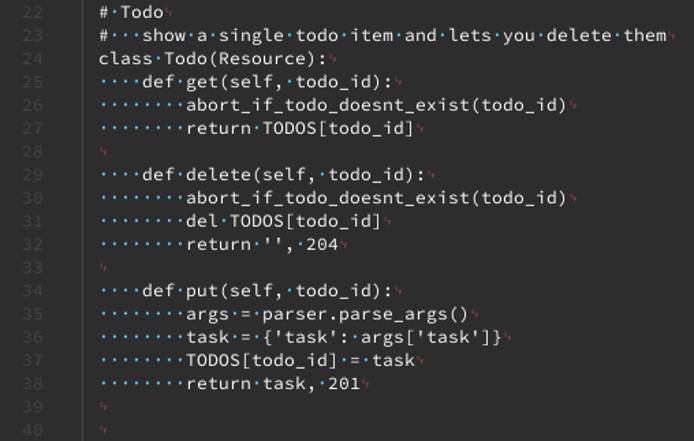
Git Integration
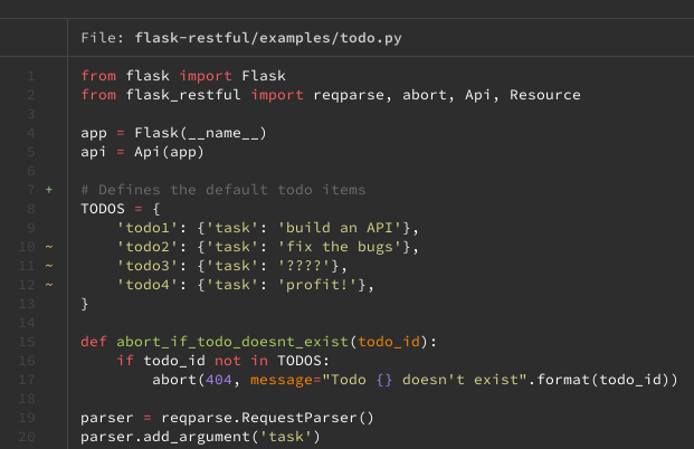
bat also integrates with Git. To see it at work, open the todo.py file with your preferred text editor, and make some changes to it. Then, open the file again with bat. You can see that bat includes Git annotations on the modified lines.
Using a command combination between Git and bat, you can even bat to view past versions of files in a Git repository.
The method uses Git’s show command, which requires you to specify a file version. Refer to the
Specifying Revisions section of Git’s revisions documentation for the various ways of doing that.
The example below looks at past commits on the todo.py file shown above. It then gets a past version of the file using one of the commit’s identifiers.
Change into the repository’s directory. This example assumes you cloned the repository to your current user’s home directory (
~).cd ~/flask-restfulGet a list of commits on the file.
git log examples/todo.pycommit 871f4e69e7758cb983056b469ec4ae40963ed1bb Author: Josh Friend <josh@example.com> Date: Mon Jul 20 09:28:15 2015 -0400 Fix examples using type=str closes #461 commit 8bdba92ef54645ada501a39edc0bc68d34127b64 Author: Josh Friend <josh@example.com> Date: Sat Mar 21 22:57:40 2015 -0400 fix references to flask.ext.* (fixes #420) commit 566431a24dac4dcf236fe06850fe96a9a3ab1890 Author: Victor Neo <victor@example.com> Date: Mon Dec 24 01:46:18 2012 +0800 Update documentation full example and sync with todo.py example. commit a4465e3e9cc4c30e7f53e0b908f734a42ed32da4 Author: Ryan Horn <ryan@example.com> Date: Tue Oct 16 21:07:16 2012 -0700 Flask-RESTfulDecide on a version you want; this example uses the earliest commit listed. Copy its commit identifier, and use that identifier in the following command:
git show a4465e3e9cc4c30e7f53e0b908f734a42ed32da4:examples/todo.py | bat -l rs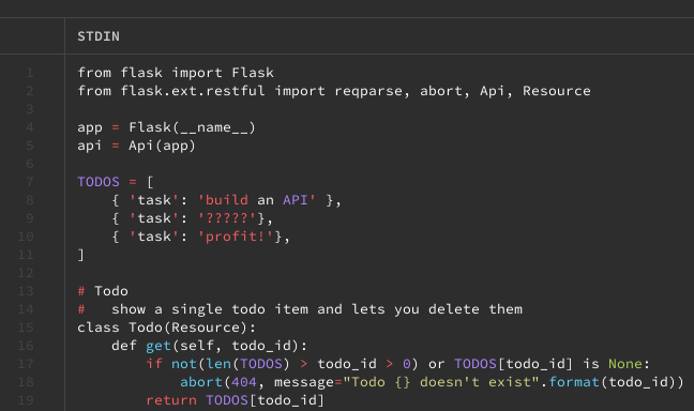
How to Customize Syntax Highlighting in bat
You can customize the syntax highlighting in bat. Whether you want a different color palette or you need to add highlighting support for a specific language, bat gives you customization options.
Set the Highlighting Theme for bat
bat comes with a host of themes for syntax highlighting. You can get a list of them, along with samples, using the command below:
bat --list-themes
To select the theme you want to use, follow one of the options listed below:
Use the
--themeflag when runningbat. With this method, you have to use the--themeflag each time you run thebatcommand.bat --theme="Solarized (dark)" ~/flask-restful/examples/todo.pySet the
BAT_THEMEenvironment variable for the shell session. This approach keeps the theme so long as your shell session is alive.export BAT_THEME="Solarized (dark)"Set the
BAT_THEMEenvironment variable in your.bashrcto make the theme selection persistent across your shell sessions.- File: ~/.bashrc
1 2 3 4[...] export BAT_THEME="Solarized (dark)"
Add Languages for Syntax Highlighting in bat
You can get a list of languages that your bat installation supports for syntax highlighting with the --list-languages option.
bat --list-languages
If bat lacks highlighting for a language you want, you can add it yourself. bat supports Sublime Text syntax files — .sublime-syntax. There is also a package manager for Sublime Text called
Package Control that is used to install packages and keep them up-to-date.
The following steps show you how to add a language once you find a .sublime-syntax file you want to use. This example uses a package found on Package Control for the
Fennel programming language.
Create a
syntaxesdirectory in thebatconfiguration directory.mkdir -p "$(bat --config-dir)/syntaxes"Place the
.sublime-syntaxfile in this directory. This example clones the Git repository for the Fennel language package, which has the syntax file in its base.cd "$(bat --config-dir)/syntaxes" git clone https://github.com/gbaptista/sublime-text-fennel.gitHave
batparse the syntax files.bat cache --buildVerify that your language option — Fennel, in this case — has been added to the list of languages in
bat.bat --list-languages[...] Fennel fnl [...]
More Information
You may wish to consult the following resources for additional information on this topic. While these are provided in the hope that they will be useful, please note that we cannot vouch for the accuracy or timeliness of externally hosted materials.
This page was originally published on





